by Debi G | Jul 25, 2016
Have you thought about this???
We’re not used to living without our smartphones, tablets and laptops for any amount of time—whether we stay indoors or go out.
But, have you ever considered that using your device outdoors could have serious consequences for your skin? Think of those old-fashioned, foil tanning reflectors to envision how screens can reflect the sun onto your face, neck and under your chin—the vulnerable spots that might not be shielded by a hat or sunscreen.
Researchers at the University of New Mexico wondered about this UV exposure from screens in natural sunlight and how it might increase cumulative UV exposure over a lifetime. As reported in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology (September 2015), they found that when a smartphone was held at close range, UV exposure increased by 36 percent!!!
Wherever you choose to spend your days, limiting your sun exposure (or avoiding it altogether) is the most effective preventative measure to protect your skin from sun damage and aging.
If you must chat, tweet or surf the internet outside, always apply a broad spectrum sunscreen, like REDEFINE Triple Defense Treatment SPF 30, or Reverse #4 so you don’t get “burned” by your smart devices. To achieve a golden glow year round without catching any UV rays while you text, try ESSENTIALS Foaming Sunless Tan. We’ve got you covered!
Be sun smart—especially if you spend a lot of screen time outdoors.


by Debi G | Feb 17, 2016
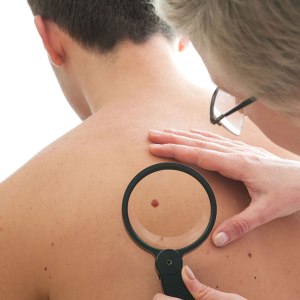
When it comes to moles and the risk of melanoma, the most serious form of skin cancer, what you don’t know could hurt you—or worse. Early detection of melanoma, before it penetrates the skin’s deep layers, is crucial and can mean the difference between life and death. Two promising breakthroughs in laser technology may soon offer doctors more efficient, biopsy-free detection methods to diagnose malignant skin cancers with more accuracy than ever.
The Dermascanner, developed by German researchers as reported in Science Daily, May 2015, combines 2D scans with additional scanned 3D data to give doctors precise details to track the growth of every individual mole from several different positions. This software also has the ability to compare current images to existing earlier scans and pinpoint the exact location of every single mole.
Meanwhile, scientists in the UK and Italy have unveiled a new laser Doppler technique that tracks fluctuations in blood flow beneath the skin over a 30-minute period, as published in Scientific Reports in August 2015. The data enables researchers to differentiate between malignant melanoma and non-cancerous moles without a biopsy.
While these advances in early skin cancer detection are promising, more research is necessary before either laser method can be used in clinical practice. Be your own health advocate between doctor visits by watching out for suspicious moles, and ask someone you trust to check any on your back. Consider downloading Mole Mapper Melanoma Study, a free iPhone app, which allows users to track changes in their moles and share the data for research.
Of course, prevention is still the best medicine for sun-related skin diseases—and it begins with you. Limit sun exposure and make broad spectrum UVA/UVB sunscreen part of your daily skincare routine. Opt for products that provide sun protection in addition to other benefits, like REDEFINE Triple Defense Treatment Broad Spectrum SPF 30 with powerful peptides to reduce the appearance of fine lines, or REVERSE Broad Spectrum SPF 50+ Sunscreen to help brighten dull skin that may be due to past sun damage.
*Information provided by Derm R+F


by Debi G | Jan 15, 2016
 Did you know?
Did you know?
In the millennia preceding the industrial revolution, pallor was popular within the upper classes, hinting at a noble life of leisure spent indoors. Dark skin was associated with poverty, hard physical work, serfdom and toiling in fields all day. Using poisonous whiteners to create pale skin has been popular throughout history – particularly during the ancient Greek, Roman and Elizabethan eras.
Tanning was only made chic, when Coco Chanel caught too much sun on a Mediterranean cruise. The photographs of her disembarking in Cannes set a new precedent of beauty; her friend Prince Jean-Louis de Faucigny-Lucigne later said: “I think she may have invented sunbathing. At that time, she invented everything.”
Fears surrounding the risks of tanning were confirmed in 2009, when it was found that rates of malignant melanoma have more than quadrupled in the past 30 years and that it is the most common form of cancer among those aged 15-34. The World Health Organization has found that people who have been using tanning devices before age 30 are 75% more likely to develop melanoma.
Who knew that Coco Chanel really could have started something so dangerous and unhealthy. If you just can’t live without that sun-kissed look, there is a better way and we have it! https://debi.myrandf.com/Shop/Product/ESST125
Message me to see how you can get a bottle free!

by Debi G | Jul 16, 2015
 Fiction: While the source of sun damage is UV radiation, the actual damage occurs for several hours following exposure. So just because you stepped out of the sun’s rays, doesn’t mean you’re in the clear when it comes to protecting your skin.
Fiction: While the source of sun damage is UV radiation, the actual damage occurs for several hours following exposure. So just because you stepped out of the sun’s rays, doesn’t mean you’re in the clear when it comes to protecting your skin.
A 2015 study at Yale University found that sunlight continues to damage people’s skin and increase the risk of cancer for four hours after they leave the beach and head indoors. The Yale team showed in the journal Science that the melanin in our skin absorbs the UV radiation and then sets off a series of chemical reactions, which release the energy—similar to what happens with fireflies when they produce light and glow with their energy.
The result is ongoing damage to the skin’s DNA for over four hours after the UV exposure. “Half or more of this kind of DNA damage is not happening on the beach,” says the lead researcher, “It’s in the car on the way home.”
Even though sun exposure may be inevitable some days, arm yourself against the harmful UV radiation by applying a broad spectrum sunscreen throughout the day, wearing protective clothing and avoiding peak UV exposure hours.
 ESSENTIALS Broad Spectrum SPF 30 Body Sunscreen
ESSENTIALS Broad Spectrum SPF 30 Body Sunscreen
Water-resistant broad spectrum UV protection for the body. Perfect for the whole family.


by Debi G | May 31, 2015

The UVA and UBA rays of the sun are the top cause of skin cancer, the most common cancer in the United States. Plus, these powerful beams can prematurely age and damage the skin. Follow these sunscreen dos and don’ts to stay safe. (Thinkstock/iStock)
http://www.weather.com/health/news/sunscreen-mistakes-youre-likely-making?cm_ven=Facebook_TheWeatherChannel_Health_JBa_Article_No_2_20150529






 Fiction: While the source of sun damage is UV radiation, the actual damage occurs for several hours following exposure. So just because you stepped out of the sun’s rays, doesn’t mean you’re in the clear when it comes to protecting your skin.
Fiction: While the source of sun damage is UV radiation, the actual damage occurs for several hours following exposure. So just because you stepped out of the sun’s rays, doesn’t mean you’re in the clear when it comes to protecting your skin.
 ESSENTIALS Broad Spectrum SPF 30 Body Sunscreen
ESSENTIALS Broad Spectrum SPF 30 Body Sunscreen

